Indicate on the graph the areas that represent the following. Q profit max 3.
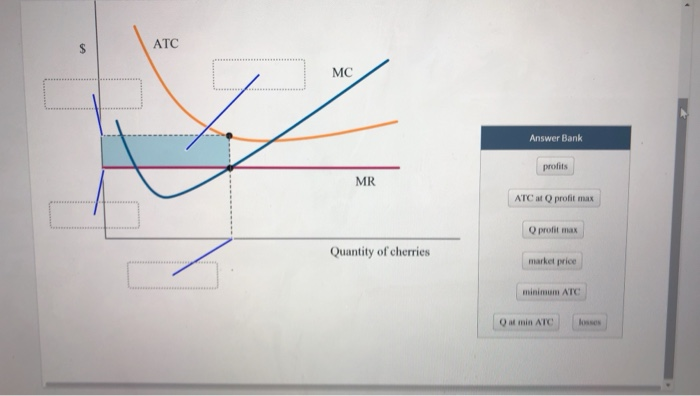
Solved The Diagram Depicts A Cost Curve Graph Of A Chegg Com
A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR MC.
. This curve throws light on the problems of scarcity and choice and illustrates the concept of opportunity cost which is a key concept for decision making and resource allocation. Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. If you are entering a negative number include a minus sign.
Blue area Deadweight welfare loss combined loss of producer and consumer surplus. 44 Page 407 The graph represents the situation of a perfectly competitive firm. Based on this graph which of the following are correct.
There are more labels than boxes. In Figure 13P-3 A highlight the firms short-run supply curve. On demand curve D the firm can sell 70 units at the price of 3000 and at price 1000 the firm can sell 40 more units of the product on D than on D.
Red area Supernormal Profit AR-AC Q. The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries. Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer.
The diagram depicts two alternative demand curves D and D for a product. There are various types of cost curves all related to each other. The average total cost ATC marginal cost MC and marginal revenue MR curves are already labeled.
There are more labels than boxes. Suppose the market price of jump drives is 7 In the graph outline an area that represents this firms losses if it produces where M RM C. The curve II 1 depicts investment of project I and QQ 1 of project Q.
As shown in the figure 43a the short run average cost curves which are also known as plant curves. D cannot be determined from the information provided. Market for Athletic Apparel 24 22 20 18 16 14 Costs and Revenues dollars 12 10 8 6 20 60 80 100 120 140 Quantity Instructions.
The average total cost ATC marginal cost MC and marginal revenue MR curves are already labeled. The average total cost ATC marginal cost MC and marginal revenue MR curves are already labeled. Long run average cost is long-run total cost divided by the level of output.
Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. This can be explained with the help of a diagram 4. The graph below depicts the revenue and cost curves for a firm operating in the athletic apparel market.
MC Isoprofit curve 40 Isoprofit curve AC 20 10 20 Quantity Q The above diagram depicts the marginal cost curve MC the average cost curve AC and the isoprofit curves of a firm. There are more labels than boxes. The rate of discount is measured along X-axis and NPV on Y-axis.
The average total cost ATC marginal cost MC and marginal revenue MR curves are already labeled. Use the accompanying diagram to graph the IS and LM curves by placing the endpoints at the correct location then place point A at the equilibrium interest rate and level of income. Enter your answer as a whole number.
A firm that is price-taking production quantity of cherries is done at the point where MR DD AR a point marked as Q in the diagram a point where profit is maximized. Diagram depicting a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently is currently operating and producing cherries. The graph depicts the long-run average total cost curve Average total cost LRATC for a firm and some possible short-run average total cost curves Get more out of your subscription Access to over 100 million course-specific study resources.
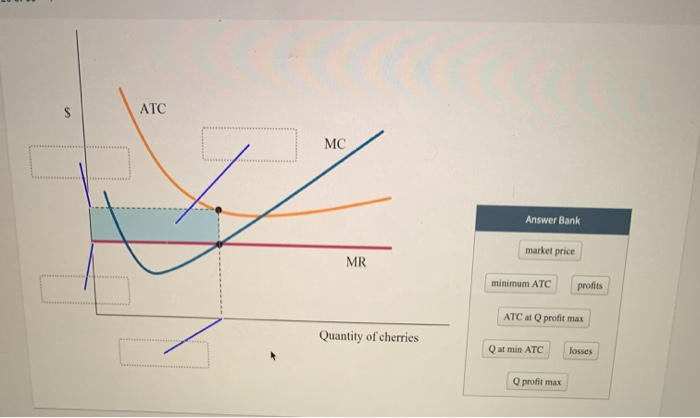
The average total cost ATC marginal cost MC and marginal revenue MR curves are already labeled. 17 The graph depicts the average total cost curve for a perfectly competitive firm. The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries.
Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. Choose the correct answers. In a free market economy productively efficient firms use these curves to find the optimal point of production where they make the most profits.
The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries. The cost curves for an individual firm are given in Figure 13P-3. The choice of project depends upon discount rate if net present values of the projects are given.
At the long-run equilib level of output this firms economic profit. This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. In Figure 13P-3 B highlight the firms long-run supply curve.
There are more labels than boxes. At point B price is and the profit is 35 200 36 240 50 250 40 240 Price P. Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer.
ATC MC Answer Bank profits MR ATC a profit max. Derive and graph the IS and LM curves. Profit or lossP-ATCQ Briefly explain whether the firm will continue to produce in the short run.
The average total cost ATC marginal cost MC and marginal revenue MR curves are already labeled. The cost curves for an individual firm are given in Figure 13P-3. Long run average cost curve depicts the least cost possible average cost for producing various levels of output.
Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. Identify each item in the graph of this cherry producer. In economics a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced.
In fact IRR depends upon social rate of discount. There are more labels than boxes. The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operatin and producing cherries.
The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries. The average total cost ATC marginal cost MC and marginal revenue MR curves are already labeled. There are more labels than boxes.
Any societys economic problems can be illustrated by using the production possibilities curve. The firm fixes a price level that is already set in the market whereby. The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries.
The diagram below depicts the cost curves for a perfectly competitive jump drive producer that is currently operating at a loss. Since it is a boundary line it is called a frontier. Compared to a competitive market the monopolist increases price and reduces output.
The diagram depicts a cost curve graph of a price-taking firm that is currently operating and producing cherries.
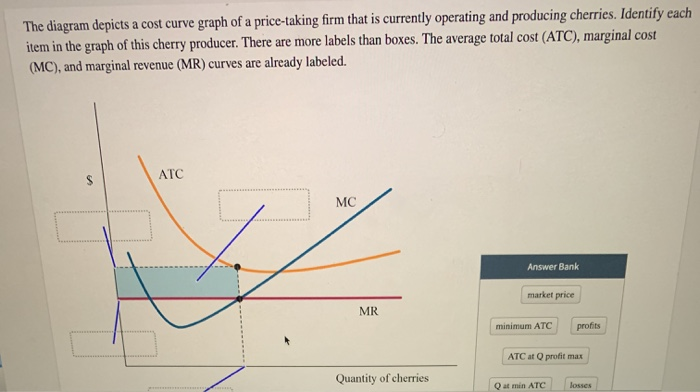
Solved The Diagram Depicts A Cost Curve Graph Of A Chegg Com

Solved The Diagram Depicts A Cost Curve Graph Of A Chegg Com
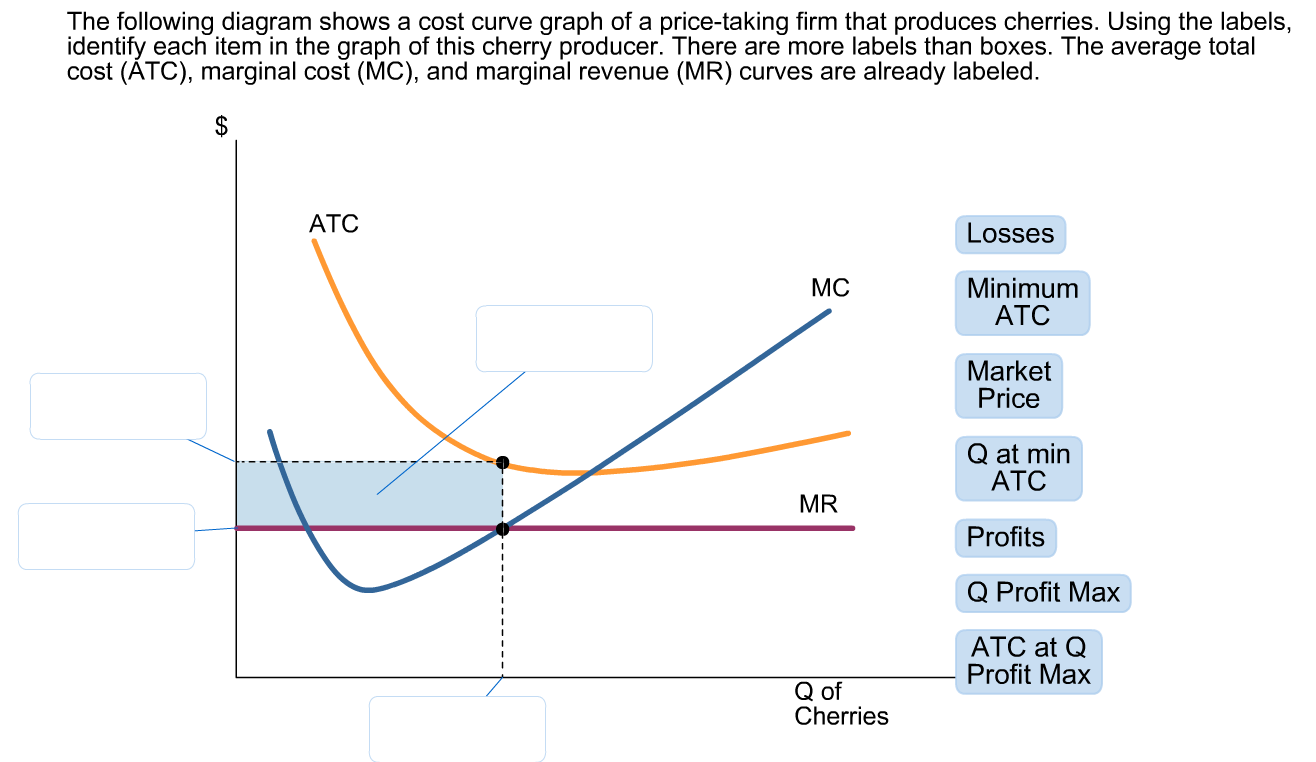
Solved The Following Diagram Shows A Cost Curve Graph Of A Chegg Com
0 Comments